A new study published in Social Science & Medicine by Prado and colleagues shows that maternal depression is the predominant persistent risk for child cognitive and social-emotional problems from early childhood to pre-adolescence.
Many studies have examined the consequences of the timing of linear growth faltering for children’s cognitive outcomes and whether catch-up in growth is associated with catch-up in cognitive development. Less is known about the timing of exposures to other risks and their developmental consequences.
This question is especially important because the middle childhood years (age 5-9) have been largely neglected in public health programs and research in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). An essential package of interventions for children age 5-14 has been proposed, which includes health interventions, such as deworming and tetanus vaccination, as well as dietary interventions, such as school feeding programs and micronutrient supplementation (Bundy et al. 2018).
In a longitudinal cohort of 359 children in Indonesia, we examined the developmental consequences of the timing of exposure to four risk factors: linear growth faltering, low hemoglobin, inadequate home environment, and maternal depressive symptoms.
We observed variation in continuity of exposure to risks from age 3.5 to 9-12 years. Some children were exposed to early risks then experienced improved conditions. Others experienced positive conditions early with late-onset risk, while others were chronically exposed to high-risk or low-risk environments.
Exposure to maternal depressive symptoms was the only risk factor that was associated with both cognitive and social-emotional problems during both early childhood and pre-adolescence. At age 9-12 y, children of mothers who had persistent high depressive symptoms showed very high social-emotional problems, more than 1 SD above the overall mean.
Early childhood home quality was also a major risk, with children in high quality homes scoring 8 IQ points above those in low quality homes.
Low hemoglobin concentration during both early childhood and pre-adolescence was associated with cognitive outcomes, but no associations were found with linear growth faltering when adjusting for other risk exposures.
While the essential package of interventions for children age 5-14 has focused on biomedical risks, supporting children to fulfill their developmental potential will require interventions that also address socio-environmental risks, such as promoting maternal mental health and responsive care and learning opportunities in the home environment.

.png)


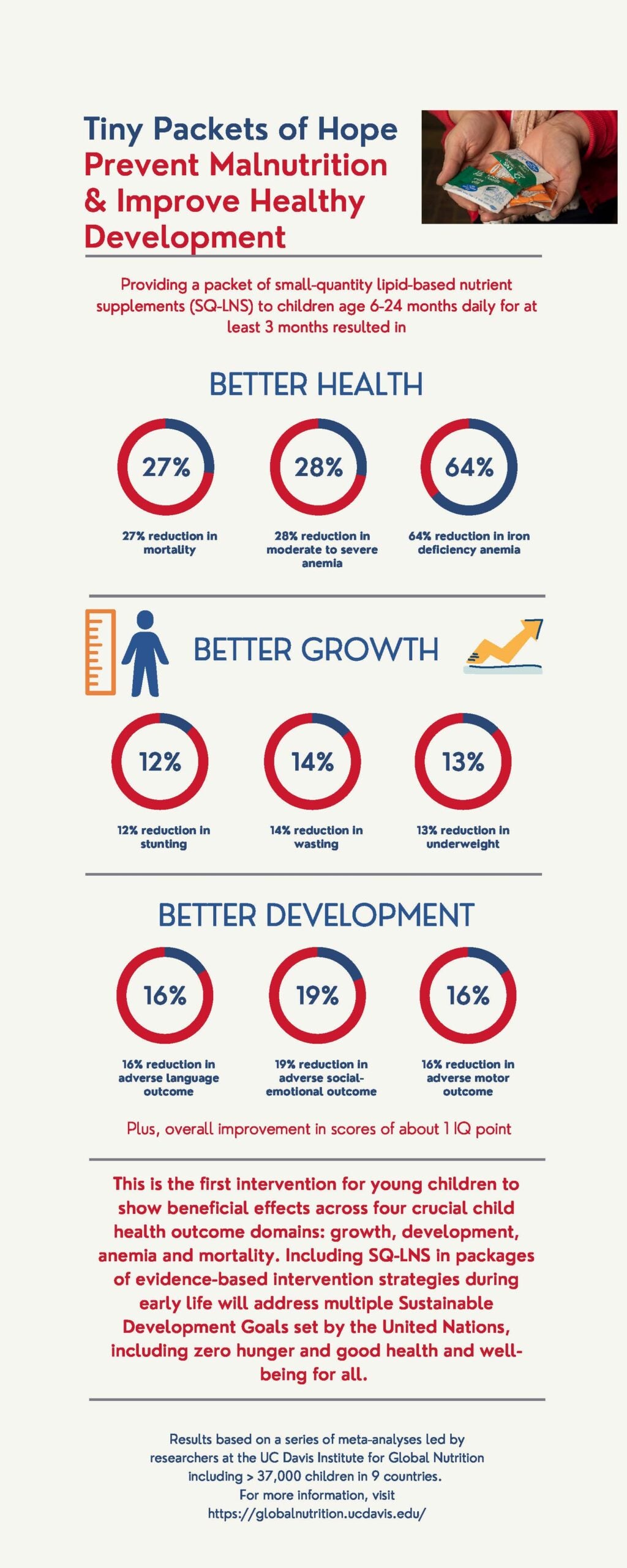
 original trial, the International Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements (iLiNS) DYAD (mother-child dyad) trial, was led by Dr. Kay Dewey at UC Davis and Dr. Anna Lartey at the University of Ghana and was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Pregnant women and children in the intervention group received lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNS), made from peanut paste, vegetable oil, and milk powder, with added vitamins and minerals. While small-quantity LNS provides only a small amount of calories per day (~118 kcal), it is packed with the vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids that are needed for children’s growth and development. In the control groups, women received a daily micronutrient capsule, similar to a pre-natal multi-vitamin, and the children did not receive any supplement.
original trial, the International Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements (iLiNS) DYAD (mother-child dyad) trial, was led by Dr. Kay Dewey at UC Davis and Dr. Anna Lartey at the University of Ghana and was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Pregnant women and children in the intervention group received lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNS), made from peanut paste, vegetable oil, and milk powder, with added vitamins and minerals. While small-quantity LNS provides only a small amount of calories per day (~118 kcal), it is packed with the vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids that are needed for children’s growth and development. In the control groups, women received a daily micronutrient capsule, similar to a pre-natal multi-vitamin, and the children did not receive any supplement.